UNIT III
What are you doing?
I´m playing the guitar.
El Presente Continuo (Present Continuous)
El presente continuo se forma con el presente simple del verbo "Be" + el verbo principal en forma "ING"
Verbos Regulares : Oraciones afirmativas
Estoy cantando
Estás cantando
Está cantando
Estamos cantando
Estáis cantando
Están cantando
Estás cantando
Está cantando
Estamos cantando
Estáis cantando
Están cantando
I am singing
You are singing
He / She / It is singingWe are singing
You are singing
They are singing
You are singing
He / She / It is singingWe are singing
You are singing
They are singing
Para formar preguntas cambiamos el orden de las palabras:
Verbos Regulares : Preguntas
¿Estoy cantando?
¿Estás cantando?
¿Está cantando?
¿Estamos cantando?
¿Estáis cantando?
¿Están cantando?
¿Estás cantando?
¿Está cantando?
¿Estamos cantando?
¿Estáis cantando?
¿Están cantando?
Am I singing?
Are you singing?
Is he / she / it singing?Are we singing?
Are you singing?
Are we singing?
Are you singing?
Is he / she / it singing?Are we singing?
Are you singing?
Are we singing?
Fíjate en el orden de las palabras en las preguntas:
IS / AM / ARE+ SUBJETO + VERBO EN ING + ?
Ahora veremos las oraciones negativas:
Verbos Regulares : Oraciones negativas
No estoy cantando
No estás cantando
No está cantando
No estamos cantando
No estáis cantando
No están cantando
No estás cantando
No está cantando
No estamos cantando
No estáis cantando
No están cantando
I am not singing
You are not singing
He / She / It is not singingWe are not singing
You are not singing
They are not singing
You are not singing
He / She / It is not singingWe are not singing
You are not singing
They are not singing
En cuanto a la forma de construir el presente continuo, todos los verbos usan la misma estructura. O sea, que no hay excepciones aunque sí, algunos verbos no se suelen usar en este tiempo verbal.
Adjetivos demostrativos
This - este, esto, esta.
That - ese, esa, eso, aquella, aquel, aquello.
These - estos, estas.
Those - esos, esas, aquell@s.
That - ese, esa, eso, aquella, aquel, aquello.
These - estos, estas.
Those - esos, esas, aquell@s.
En general el uso de los adjectivos demostrativos en inglés es igual que en el español. Hay que recordar que no existen formas masculinas/femininas, y nada más.
Abajo tienes un ejemplo de los plurales:

FUENTE: Inglés/Madrid
UNIT II - PRESENT SIMPLE
Los dos usos
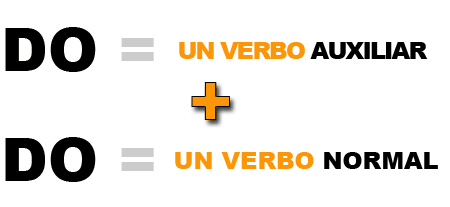
El verbo "do" tiene 2 funciones
- Es el verbo "hacer" (¿facíl no?)
- Es un verbo auxiliar
- Un verbo auxiliar es un verbo que usamos para formar tiempos verbales.
- Do/Does se usa para formar preguntas en el presente simple.
- Don't/Doesn't se usa para formar frases negativas en el presente simple.
USE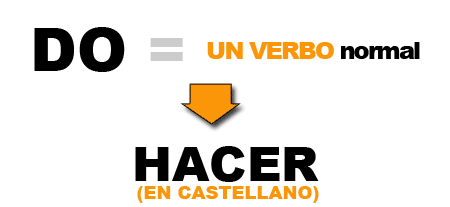
Cuando "do" es un verbo normal, significa "hacer"- I do many things. - Hago muchas cosas.
- She does few things. - Ella hace pocas cosas.
- I do my homework. - Hago mis deberes.
Do: el verbo auxiliar

Usamos "do"/"does" para formar preguntas en el presente simple*
- Do you play? - ¿Juegas?
- Does Juan play? - ¿Juega Juan?
- Do they play? - ¿Juegan? (ell@s)
- When do you eat? - ¿Cuándo comes?
- Do/Does + SUJETO** + VERBO (INFINITVO) + ?
Usamos "don't"/"doesn't" ("do not" / "does not") para formar todas*** las frases negativas en el presente simple.
- I don't play - No juego
- She doesn't eat - (Ella) no come
Listening
Do you play?
Do they play?
She doesn't eat.
Do they play?
She doesn't eat.
FUENTE: Inglés/Madrid
And study for your exams! ; )
Listening 1 Repeated Actions
We use the Simple Present to express the idea that an action is repeated or usual. The action can be a habit, a hobby, a daily event, a scheduled event or something that often happens. It can also be something a person often forgets or usually does not do.
FORM
(Affirmative)
Subject (I, you, we and they) + verb+ complements.
Subject (he, she, it)+ verb+ s/es + complements.
Examples:
- You walk the dog everyday.
- She walks the dog everyday.
Subject (I, you, we and they) + don't (do not) + verb+ complements.
Subject (he, she, it) + doesn't (does not) + verb+complements.
Examples:
- You don't walk the dog everyday.
- She doesn't walk the dog everyday.
Do + subject (I, you, we and they) + verb+ complements?


Does + subject (he, she, it)+ verb+ s/es + complements?
Examples:
- Do you walk the dog?
- Does she walk the dog?
Examples:
- I play tennis.
- She does not play tennis.
- Does he play tennis?
- The train leaves every morning at 8 AM.
- The train does not leave at 9 AM.
- When does the train usually leave?
- She always forgets her purse.
- He never forgets his wallet.
- Every twelve months, the Earth circles the Sun.
- Does the Sun circle the Earth?
USE 2 Facts or Generalizations

The Simple Present can also indicate the speaker believes that a fact was true before, is true now, and will be true in the future. It is not important if the speaker is correct about the fact. It is also used to make generalizations about people or things.
Examples:
- Cats like milk.
- Birds do not like milk.
- Do pigs like milk?
- California is in America.
- California is not in the United Kingdom.
- Windows are made of glass.
- Windows are not made of wood.
USE 3 Scheduled Events in the Near Future

Speakers occasionally use Simple Present to talk about scheduled events in the near future. This is most commonly done when talking about public transportation, but it can be used with other scheduled events as well.
Examples:
- The train leaves tonight at 6 PM.
- The bus does not arrive at 11 AM, it arrives at 11 PM.
- When do we board the plane?
- The party starts at 8 o'clock.
- When does class begin tomorrow?
(by teacher María José)
PREPOSITIONS IN ON AT
AUXILIARES DE TIEMPO DO / DOES / DID
PREPOSITIONS IN ON AT
AUXILIARES DE TIEMPO DO / DOES / DID




